In 2026, there will be four eclipses: two solar eclipses and two lunar eclipses
| Date | Type | Visibility |
| 17 February 2026 | Annular solar eclipse | Not visible in Belgium |
| 3 March 2026 | Total lunar eclipse | Not visible in Belgium |
| 12 August 2026 | Total solar eclipse | In one part of Belgium visible as a partial eclipse. In one part of Belgium partially visible as a partial eclipse. |
| 28 August 2026 | Partial lunar eclipse | Partially visible in Belgium |
I – 17 February 2026 – Annular solar eclipse, not visible in Belgium
| Phase | Universal time | Longitude | Latitude |
| Start eclipse | 09h56.4 | 079 53 W | 62 14 S |
| Start annular eclipse | 11h43.0 | 144 56 E | 73 38 S |
| Start central eclipse | 11h48.3 | 136 35 E | 71 56 S |
| Maximum of the eclipse | 12h13.5 | 086 23 E | 63 56 S |
| End central eclipse | 12h36.1 | 099 03 E | 50 08 S |
| End annular eclipse | 12h41.4 | 096 50 E | 47 33 S |
| End eclipse | 14h27.7 | 059 29 E | 12 24 S |
The map below shows the region where the eclipse is observable. The explanation of the codes used can be found at the bottom of the page.
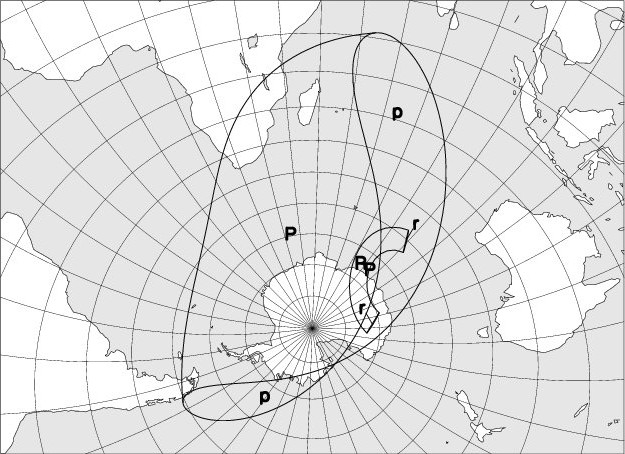
Maximum size of the eclipse: 0.964, the diameter of the solar disc being taken as the unit.
II – 3 March 2026 – Total lunar eclipse, not visible in Belgium
| Phase | Universal time | Longitude | Latitude | Position angle | Altitude at Uccle/Ukkel |
| Start penumbral eclipse | 08h42.8 | 129 12 W | 07 08 N | 104 E | – |
| Start partial lunar eclipse | 09h49.7 | 145 25 W | 06 51 N | 096 E | – |
| Start total lunar eclipse | 11h04.0 | 163 26 W | 06 32 N | 064 E | – |
| Maximum of the eclipse | 11h33.7 | 170 37 W | 06 24 N | 028 E | – |
| End total lunar eclipse | 12h03.3 | 177 49 W | 06 16 N | 353 E | – |
| End partial lunar eclipse | 13h17.6 | 164 11 E | 05 57 N | 320 E | – |
| End penumbral eclipse | 14h24.7 | 147 55 E | 05 40 N | 312 E | – |
The longitude and the latitude refer to the point on Earth where the Moon is at that time at its zenith. The position angle is defined from the imaginary line that connects the center of the lunar disc to the center of the Earth’s shadow. It is measured at the center of the lunar disc, from the North, in an anti-clockwise direction. At the beginning and at the end of the penumbra and shadow phases, it is the position angle of the contact point. The altitude and times of the Moon’s rise and fall are calculated for its center, without taking refraction into account.
Magnitude of the eclipse: 1.155, the diameter of the lunar disk being taken as the unit.
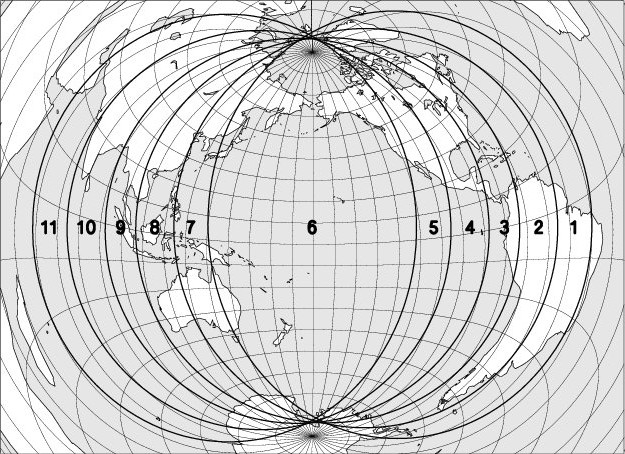
The map below shows the region where the eclipse is observable. The explanation of the codes used can be found at the bottom of the page.
III – 12 August 2026 – Total solar eclipse, in one part of Belgium visible as a partial eclipse, in one part of Belgium partially visible as a partial eclipse
| Phase | Universal time | Longitude | Latitude |
| Start of the eclipse | 15h34.2 | 166 25 W | 56 31 N |
| Start of the total eclipse | 16h58.1 | 117 54 E | 75 11 N |
| Start of the central eclipse | 17h00.1 | 113 29 E | 75 05 N |
| Maximum of the eclipse | 17h03.9 | 105 17 E | 85 06 N |
| Central eclipse at local apparent noon | 17h44.4 | 025 35 W | 65 59 N |
| End of the central eclipse | 18h32.2 | 005 24 E | 38 40 N |
| End of the total eclipse | 18h34.2 | 004 11 E | 37 51 N |
| End of the eclipse | 19h58.0 | 024 56 W | 11 21 N |
The map below shows the region where the eclipse is observable. The explanation of the codes used can be found at the bottom of the page.
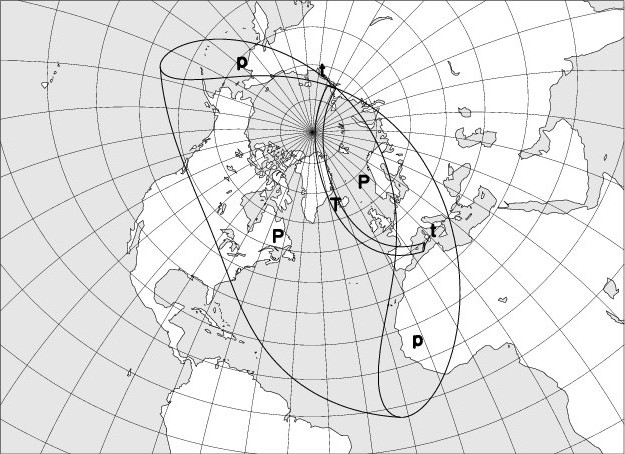
The duration of the totality phase along the centrality line will reach a maximum of 2m 21s at a point located at 26° of longitude west and 66° of latitude north.
Phases in Uccle/Ukkel – Brussels (Observatory)
| Phase | Universal time | Position angle relative to the pole | Position angle relative to the zenith | Altitude at Uccle/Ukkel |
| First contact | 17h18min53s | 292 | 251 | +16 |
| Maximum of the eclipse | 18h13min41s | 207 | 168 | +7 |
| Sunset | 19h03min13s | 122 | 086 | 0 |
Magnitude of the eclipse: 0.911, the diameter of the solar disk being taken as the unit.
The position angle relative to the pole, resp. the zenith, is the angle formed by the direction of the centre of the lunar disc with the direction of the pole, resp. the zenith. Both angles are measured at the centre of the solar disc in an anti-clockwise direction. At the beginning and at the end of the eclipse, they correspond to the position angles of the contact points.
The altitude of the Sun is that of a reference point, which is located during the eclipse in the eclipsed part of the Sun, and which coincides with the times of contact with the point of contact of the Sun and Moon. Refraction is not taken into account.
The table below gives the phases for some representative Belgian sites.
In Brussels and Wallonia
| Location | Start in universal time | Maximum in universal time | End in universal time | Magnitude | Local circumstances |
| Brussels | 17h18min48s | 18h13min36s | 19h03min22s (*) | 0.911 | 2 |
| Nivelles/Nijvel | 17h19min14s | 18h14min01s | 19h02min48s (*) | 0.912 | 2 |
| Jodoigne/Geldenaken | 17h19min02s | 18h13min41s | 19h00min57s (*) | 0.910 | 2 |
| Tournai/Doornik | 17h19min12s | 18h14min13s | 19h06min21s | 0.916 | 1 |
| Mons/Bergen | 17h19min29s | 18h14min20s | 19h03min54s (*) | 0.915 | 2 |
| Charleroi | 17h19min34s | 18h14min18s | 19h01min48s (*) | 0.913 | 2 |
| Chimay | 17h20min12s | 18h14min55s | 19h01min21s (*) | 0.916 | 2 |
| Philippeville | 17h19min56s | 18h14min38s | 19h00min48s (*) | 0.914 | 2 |
| Namur/Namen | 17h19min30s | 18h14min08s | 19h00min16s (*) | 0.911 | 2 |
| Dinant | 17h19min50s | 18h14min26s | 18h59min31s (*) | 0.912 | 2 |
| Gedinne | 17h20min19s | 18h14min53s | 18h58min40s (*) | 0.914 | 2 |
| Huy/Hoei | 17h19min23s | 18h13min56s | 18h58min54s (*) | 0.909 | 2 |
| Liège/Luik | 17h19min10s | 18h13min39s | 18h57min54s (*) | 0.907 | 2 |
| Werbomont | 17h19min37s | 18h14min03s | 18h56min43s (*) | 0.909 | 2 |
| Eupen | 17h19min11s | 18h13min33s | 18h56min01s (*) | 0.906 | 2 |
| Sankt Vith | 17h19min47s | 18h14min06s | 18h54min40s (*) | 0.908 | 2 |
| Marche-en-Famenne | 17h19min53s | 18h14min23s | 18h57min41s (*) | 0.911 | 2 |
| Bastogne/Bastenaken | 17h20min17s | 18h14min39s | 18h55min33s (*) | 0.911 | 2 |
| Libramont | 17h20min26s | 18h14min53s | 18h56min42s (*) | 0.913 | 2 |
| Bouillon | 17h20min39s | 18h15min09s | 18h57min38s (*) | 0.914 | 2 |
| Virton | 17h21min02s | 18h15min25s | 18h55min09s (*) | 0.914 | 2 |
| Arlon/Aarlen | 17h20min50s | 18h15min09s | 18h54min21s (*) | 0.912 | 2 |
In Flanders:
| Location | Start in universal time | Maximum in universal time | End in universal time | Magnitude | Local circumstances |
| Veurne | 17h18min20s | 18h13min35s | 19h05min56s | 0.916 | 1 |
| Oostende/Ostende | 17h18min05s | 18h13min17s | 19h05min37s | 0.914 | 1 |
| Brugge/Bruges | 17h18min07s | 18h13min14s | 19h05min30s | 0.913 | 1 |
| Poperinge | 17h18min43s | 18h13min56s | 19h06min15s | 0.917 | 1 |
| Kortrijk/Courtrai | 17h18min48s | 18h13min52s | 19h06min04s | 0.915 | 1 |
| Gent/Gand | 17h18min25s | 18h13min24s | 19h05min32s | 0.912 | 1 |
| Oudenaarde/Audenarde | 17h18min47s | 18h13min46s | 19h05min54s | 0.914 | 1 |
| Geraardsbergen/Grammont | 17h18min55s | 18h13min49s | 19h05min01s (*) | 0.913 | 2 |
| Aalst/Alost | 17h18min38s | 18h13min31s | 19h04min53s (*) | 0.911 | 2 |
| Sint-Niklaas/Saint-Nicolas | 17h18min14s | 18h13min07s | 19h05min08s (*) | 0.910 | 2 |
| Mechelen/Malines | 17h18min29s | 18h13min16s | 19h03min22s (*) | 0.909 | 2 |
| Antwerpen/Anvers | 17h18min08s | 18h12min58s | 19h04min13s (*) | 0.908 | 2 |
| Essen | 17h17min42s | 18h12min33s | 19h04min36s | 0.907 | 1 |
| Turnhout | 17h17min58s | 18h12min41s | 19h02min19s (*) | 0.906 | 2 |
| Geel | 17h18min15s | 18h12min56s | 19h01min41s (*) | 0.907 | 2 |
| Neerpelt | 17h18min08s | 18h12min43s | 19h00min06s (*) | 0.905 | 2 |
| Hasselt | 17h18min40s | 18h13min14s | 18h59min38s (*) | 0.907 | 2 |
| Tongeren/Tongres | 17h18min55s | 18h13min27s | 18h58min43s (*) | 0.907 | 2 |
| Maaseik | 17h18min22s | 18h12min51s | 18h58min16s (*) | 0.904 | 2 |
| Leuven/Louvain | 17h18min45s | 18h13min28s | 19h02min03s (*) | 0.909 | 2 |
| Diest | 17h18min34s | 18h13min13s | 19h00min57s (*) | 0.907 | 2 |
The local circumstances are given as follows:
1 Eclipse visible as partial eclipse.
2 Eclipse partially visible as partial eclipse.
Data marked as (*) concerns the sunset.
IV – 28 August 2026 – Partial lunar eclipse, partially visible in Belgium
| Phase | Universal time | Longitude | Latitude | Position angle | Altitude at Uccle/Ukkel |
| Start penumbral eclipse | 01h22.2 | 021 42 W | 09 59 S | 081 E | +24 |
| Start partial eclipse | 02h33.5 | 038 59 W | 09 42 S | 092 E | +18 |
| Maximum of the eclipse | 04h12.9 | 063 06 W | 09 18 S | 153 E | +06 |
| Moonset at Uccle/Ukkel | 04h52.6 | 072 44 W | 09 09 S | 188 E | 0 |
| End partial eclipse | 05h52.3 | 087 14 W | 08 54 S | 213 E | – |
| End penumbral eclipse | 07h03.4 | 104 29 W | 08 37 S | 225 E | – |
The longitude and the latitude refer to the point on Earth where the Moon is at that time at its zenith. The position angle is defined from the imaginary line that connects the center of the lunar disc to the center of the Earth’s shadow. It is measured at the center of the lunar disc, from the North, in an anti-clockwise direction. At the beginning and at the end of the penumbra and shadow phases, it is the position angle of the contact point. The altitude and times of the Moon’s rise and fall are calculated for its center, without taking refraction into account.
Magnitude of the eclipse: 0.935, the diameter of the lunar disk being taken as the unit.
The map below shows the region where the eclipse is observable. The explanation of the codes used can be found at the bottom of the page.
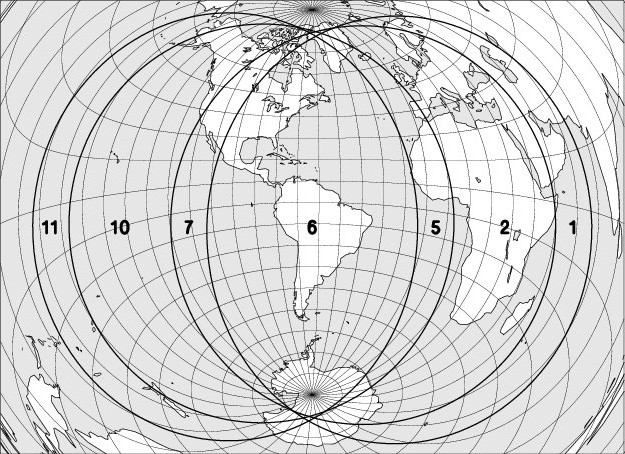
Explanations :
The codes used on the maps to indicate the moon eclipse visibility are: entry into the darkness is visible in regions 1 to 6, entry into the darkness in regions 2 to 7, the beginning of the totality in regions 3 to 8. The exits of the totality, the shadow and the penumbra are respectively observable in regions 4 to 9, 5 to 10, and 6 to 11. In region 6, the entire eclipse can be observed, in regions 5 to 7 the umbral phases are observable; in regions 4 to 8 the totality is fully visible.
On solar eclipse visibility maps, the following codes are used:
“P”: Partial eclipse of the Sun, visible.
“p”: Partial eclipse of the Sun, partly visible.
“R”: Annular eclipse, whose annular phase is fully observable.
“r”: Annular eclipse, whose annular phase is partially observable.
“T”: Total eclipse, whose totality phase is fully observable.
“t”: Total eclipse, whose totality phase is partially observable.
The basic data used to write the eclipse chapter were borrowed from the DE440 digital integration, kindly provided by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. To move from Terrestrial Time (TT) to Universal Time (UT), the following provisional relationship was used:
UT = TT – 69.0 s
